Page 19 - Annual Report 2023
P. 19
Power Market Annual Report 1401 15
Power Market Annual Report 1401 19
6. Fuel Consumption 4. Ancillary Services
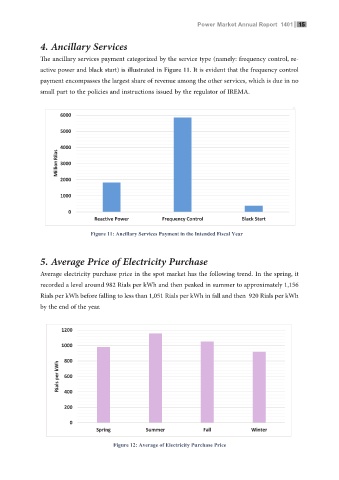
Figure 13 illustrates how much fuel was consumed by thermal power plants in fiscal year. It is The ancillary services payment categorized by the service type (namely: frequency control, re-
dropped from about 23.55 Billion Cubic Meters in summer to 9.96 Billion Cubic
clear that natural gas was the dominant primary energy in Iran power generation sector. The active power and black start) is illustrated in Figure 11. It is evident that the frequency control
Meters in winter. The annual natural gas consumption increased by 2.4%
annual natural gas consumption increased by 2.4% compared to the last fiscal year. payment encompasses the largest share of revenue among the other services, which is due in no
compared to the last fiscal year.
As regards liquid fuel consumption, it dropped to its lowest level in spring and then gradually small part to the policies and instructions issued by the regulator of IREMA.
As regards liquid fuel consumption, it dropped to its lowest level in spring which
reached its peak in winter.
and then gradually reached its peak in winter.
60
6000
00
30,000 6000
00
50
5000
25,000
5000
Bilion Cubic Meter/Billion Liter 20,000 MillionRilas Milion Rilas 4000
40
4000
00
00
3000
30
15,000
3000
Milion
00
2000
20
10,000
2000
10
00
1000
5,000
1000
0 0
Reactive Power r Frequency Control l Black Start t
C
cy
reque
F
n
ar
o
tiv
t
e
r
o
we
n
P
t
c
k
a
Re
B
l
S
o
ac
‐ 0
Spring Summer Fall Winter
Frequency Control
Reactive Power
e I
r
1
y
1
a
An
:
cill
S
ymen
Pa
in th
t
ices
rv
e
Figure 11: Ancillary Services Payment in the Intended Fiscal Year Black Start
Figure
d
Fi
d
e
sc
Yea
r
a
l
n
e
n
t
Natural Gas (B.m3) Gasoline (B.L) Mazut (B.L)
5. Average Price of El
Figure 11:
5. Average Price of El
5. Average Price of Electricity Purchase a s th e follo w ing trend . In
Figure 13: Volume of the Fuel Consumption in the Intended Fiscal Year
Average electricity purchase price in the spot market has the following trend. In
sp
ice in the
Av
rket h
u
a
r
rchase pr
e
g
tricity p
ot ma
e elec
5. Average Price of Electricity Purchase
the
it re
e
the spring time, it recorded a level around 982 Rials per kWh and then peaked in
e
o
rded a le
k
c
v
d
in
t
r kWh
i
m
und 98
p
ring
sp
e
2 Rials
and then pea
,
l aro
e
7. Transmission Cost Average electricity purchase price in the spot market has the following trend. In the spring, it
Average electricity purchase price in the spot market has the following trend. In
1,05
ore fallin
1
to
bef
le
56
e
als p
Ri
an
g
r kWh
ss th
o
r
mmer
x
summer at to approximately 1,156 Rials per kWh before falling to less than 1,051
su
at to
app
imately 1,1
the spring time, it recorded a level around 982 Rials per kWh and then peaked in
Since the RECs are the owners of the transmission system in IREMA, recorded a level around 982 Rials per kWh and then peaked in summer to approximately 1,156
1
k
s per kWh
l
year.
Wh
by
the
d
e
the e
n
o
f
p
r
ll and th
92
u
h
o
e
n
l
d
s
in fa
Rials per kWh in fall and then 920 Rials per kWh by the end of the year. It should
Rials
I
t
0 Ria
summer at to approximately 1,156 Rials per kWh before falling to less than 1,051
the transmission cost is paid to them by all market participantsto Rials per kWh before falling to less than 1,051 Rials per kWh in fall and then 920 Rials per kWh
be noted that the price in fall was higher than the price in spring.
ted
be n
n
spring
.
o
w
ice in fall
the price i
n
a
the pr
s higher th
a
th
a
t
Rials per kWh in fall and then 920 Rials per kWh by the end of the year. It should
remunerate their costs. According to the fFigure 14, the highest amount by the end of the year.
12
1200
00
of transmission cost was recorded in spring while due to the reduction be noted that the price in fall was higher than the price in spring.
of cross-border exchanges the lowest amount was observed in summer 10 1200
1000
00
time.
00
800
8 1000
Rials per kWh Rials per kWh Rials per kWh 600
00
6 800
400
00
4 600
00
200
2 400
0 0
200
e
m
Spring
Wint
S p r i n g S Summer r Fall l Winter r
um
l
F
e
a
0
e
ag
El
Figure 12: Average of Electricity Purchase Price
of
Spring Fi g u r e 1 2: Av er Summer ec t r i c i t y P u rc has e Pri c e Winter
Fall
6. Fuel Consumpti o n
6. Fuel Consumption
Figure 12: Average of Electricity Purchase Price
1 Regional Electricity Company
Figure 13 illustrates how much fuel was consumed by thermal power plants in
Figu re 1 3 illustra tes ho w much fuel wa s c o nsu m e d by therma l po we r pla n ts in
6. Fuel Consumption
fiscal year. It is clear that natural gas was the dominant primary energy in Iran
14 fisc al year. It is c l ear that natural gas wa s th e dominant p r imary ene r gy in Ira n
Figure 13 illustrates how much fuel was consumed by thermal power plants in
power generation sectorsource from which the energy was produced. Although it
p o w e r ge ne ra tio n se ct or so ur c e f r o m wh ic h t h e e n e r gy w a s p r o d u c e d . Althou gh it
fiscal year. It is clear that natural gas was the dominant primary energy in Iran
power generation sectorsource from which the energy was produced. Although it
13 13
13